Many screenplay writers use a common phrase to signal the end of their film: “fade to black.”
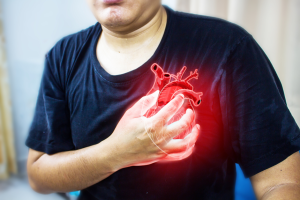
After his 2023 heart surgery, 67-year-old Herman Johansen - an actor and writer - is determined that his show must go on.
Johansen grew up in Billings, Missouri and earned his Bachelor of Fine Arts in Acting from (Southwest) Missouri State University, a school known for producing film and Broadway actors. He stayed in the area, married and raised two children: Nathan and Cassandra.